Robots in the medical field are transforming how surgeries are performed, streamlining supply delivery and disinfection, and freeing up time for providers to engage with patients.
Emerging in the 1980s, the first robots in the medical field offered surgical assistance via robotic arm technologies. Over the years, artificial intelligence (AI)–enabled computer vision and data analytics have transformed health robotics, expanding capabilities into many other areas of healthcare.
Robots are now used not only in the operating room, but also in clinical settings to support health workers and enhance patient care. During the COVID-19 pandemic, hospitals and clinics began deploying robots for a much wider range of tasks to help reduce exposure to pathogens. It’s become clear that the operational efficiencies and risk reduction provided by health robotics offer value in many areas.
For example, robots can clean and prep patient rooms independently, helping limit person-to-person contact in infectious disease wards. Robots with AI-enabled medicine identifier software reduce the time it takes to identify, match, and distribute medicine to patients in hospitals.
As technologies evolve, robots will function more autonomously, eventually performing certain tasks entirely on their own. As a result, doctors, nurses, and other healthcare workers can focus on providing more empathy in patient care.
BENEFITS OF ROBOTICS IN HEALTHCARE
Health robotics enable a high level of patient care, efficient processes in clinical settings, and a safe environment for both patients and health workers.
High-Quality Patient Care
Medical robots support minimally invasive procedures, customized and frequent monitoring for patients with chronic diseases, intelligent therapeutics, and social engagement for elderly patients. In addition, as robots alleviate workloads, nurses and other caregivers can offer patients more empathy and human interaction, which can promote long-term well-being
Operational Efficiencies
Service robots streamline routine tasks, reduce the physical demands on human workers, and ensure more consistent processes. These robots can keep track of inventory and place timely orders, helping make sure supplies, equipment, and medication are where they are needed. Mobile cleaning and disinfection robots allow hospital rooms to be sanitized and readied for incoming patients quickly.
Safe Work Environment
Service robots help keep healthcare workers safe by transporting supplies and linens in hospitals where pathogen exposure is a risk. Cleaning and disinfection robots limit pathogen exposure while helping reduce hospital acquired infections (HAIs)—and hundreds of healthcare facilities are already using them.1 Social robots also help with heavy lifting, such as moving beds or patients, which reduces physical strain on healthcare workers.
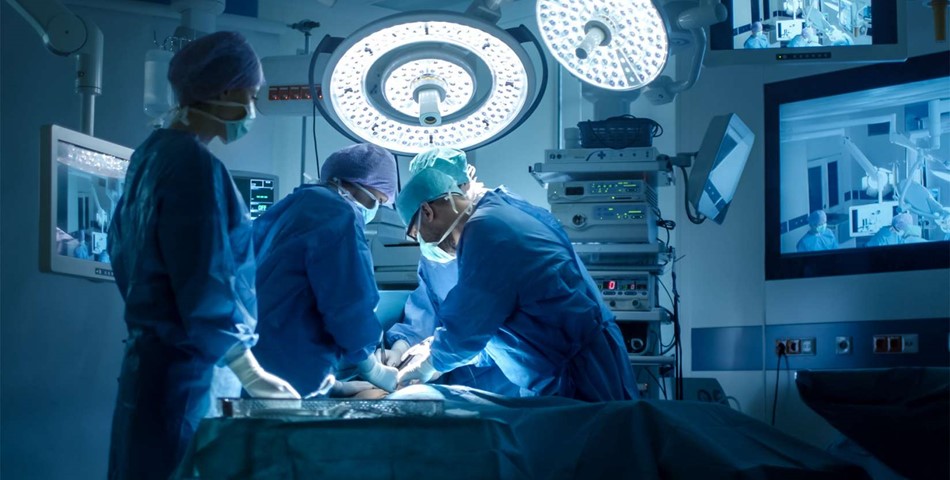
SURGICAL-ASSISTANCE ROBOTS
As motion control technologies have advanced, surgical-assistance robots have become more precise. These robots help surgeons perform complex microprocedures without making large incisions. As surgical robotics continue to evolve, AI-enabled robots will eventually use computer vision to navigate to specific areas of the body while avoiding nerves and other obstacles. Some surgical robots may even be able to complete tasks autonomously, allowing surgeons to oversee procedures from a console.
Surgeries performed with robotics assistance fall into two main categories:
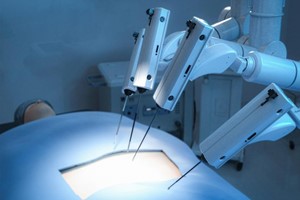
Minimally invasive surgeries for the torso. These include robotic hysterectomy, robotic prostatectomy, bariatric surgery, and other procedures primarily focused on soft tissues. After insertion through a small incision, these robots lock themselves into place, creating a stable platform from which to perform surgeries via remote control. Open surgery using large incisions was once the norm for most internal procedures. Recovery times were much longer, and the potential for infection and other complications was greater. Working manually through a button-sized incision is extremely difficult, even for an experienced surgeon. Surgical robots, such as the da Vinci robot by Intuitive, make these procedures easy and accurate, with a goal to reduce infections and other complications.
Orthopedic surgeries. Devices like the Mako robot by Stryker can be preprogrammed to perform common orthopedic surgeries, such as knee and hip replacements. Combining smart robotic arms, 3D imaging, and data analytics, these robots enable more predictable results by employing spatially defined boundaries to assist the surgeon. AI modeling enables the Mako robot to be trained in specific orthopedic surgeries, with precise direction for where to go and how to perform the procedures.
The ability to share a video feed from the operating room to other locations—near or far—allows surgeons to benefit from consultations with other specialists leading their field. As a result, patients have the best surgeons involved in their procedures.
The field of surgical robotics is evolving to make greater use of AI. Computer vision enables surgical robots to differentiate between types of tissue within their field of view. For example, surgical robots now have the ability to help surgeons avoid nerves and muscles during procedures.2 High-definition 3D computer vision can provide surgeons with detailed information and enhanced performance during procedures. Eventually, robots will be able to take over small subprocedures, such as suturing or other defined tasks under the watchful gaze of the surgeon.
Robotics plays a key role in surgeon training as well. The Mimic Simulation Platform, for example, uses AI and virtual reality to provide surgical robotics training to new surgeons. Within the virtual environment, surgeons can practice procedures and hone skills using robotics controls.